Nature Reviews Nephrology Publication for Matthias Wuttke
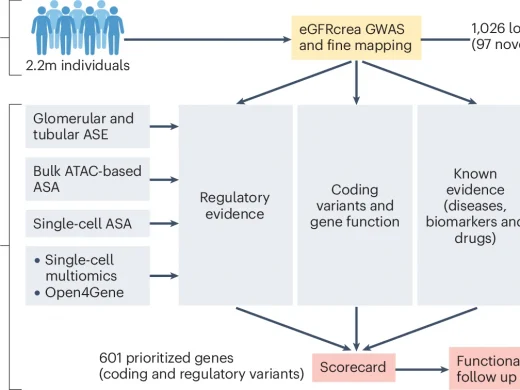
GWAS scorecard prioritizes kidney genes using coding and regulatory variants
Kidney disease represents a global public health challenge. Chronic kidney disease alone affects 10-15% of adults and increases the risk for kidney failure, adverse cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality. Despite the high prevalence and the great costs associated with treating kidney diseases, the low number of clinical trials and specific treatments in nephrology attests to a shortage of therapeutic targets. The identification of druggable targets has been hampered by an incomplete understanding of the mechanisms underlying the etiology and progression of kidney diseases. Pharmacological compounds that operate on proteins or pathways connected to a given disease by human genetic evidence are at least twice as likely to gain approval, compared to those without genetic support. Therefore, the long-term vision of the CRC 1453 is to use evidence from genetic kidney diseases to identify, characterize, and modify molecules and pathways that represent targets to improve the prevention and treatment of kidney disease.